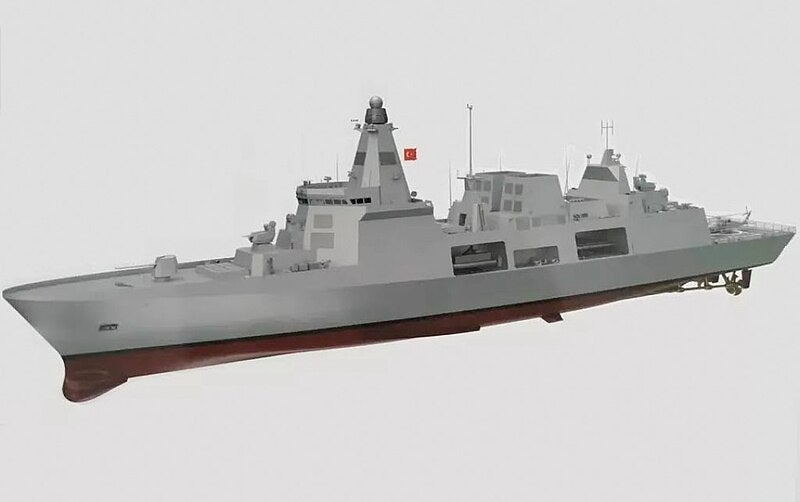
Turkey Is Making Changes To The Design of The Planned TF-2000 Air Defense Destroyer
A delegation led by Turkish Naval Forces Commander Admiral Ercüment Tatlıoğlu recently visited the Istanbul Shipyard Command and Naval Forces Design Project Office (DPO). The purpose of the visit was to review the design and road map of the TF-2000 destroyer, which represents the third phase of the MİLGEM Project, and to examine the new aircraft carrier concept design. After Admiral Tatlıoğlu’s visit, new developments regarding the features and design of the TF-2000 were shared in the images shared on the X account of the Ministry of National Defense (MSB).
The first thing that stands out about the TF-2000’s new design is the update of previously announced features such as length, width, and displacement. Previously, the TF-2000 Destroyer was described as having an overall length of 166m, a width of 21.5m, a displacement of 8,500 tons, and a top speed of 28+ knots. The ship’s width remained nearly unchanged in the updated design, but its length was reduced to 149 meters and its displacement to 8,300 tons. It was also decided that the new design would forego the split chimney system, reduce the maximum speed to 26+ knots, and use a CODOG type main propulsion system consisting of two gas turbines and two main diesel engines.
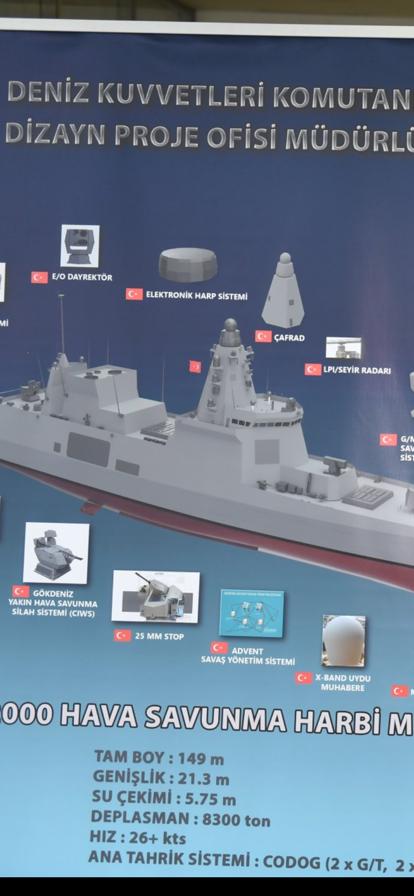

Another significant aspect of the new design that drew attention was the change in weapon systems used in the TF-2000. While previous statements said that the TF-2000 would have 64 VLS cells, the new design will have 96 VLS cells, 32 in the bow behind the main gun and 64 in the center of the ship. Air defense missiles like SİPER and HİSAR-D RF can be launched from these cells. Furthermore, the ATMACA anti-ship missile launchers, which were planned to be installed on the ship’s bridge in the previous version, are not included in the new design. The removed Atmaca anti-ship missiles are expected to be launched from MİDLAS Vertical Launch System (VLS) Cells in the future. Other weapon systems included in the updated design of the TF-2000 destroyer include a 127mm gun, Aselsan’s 25mm STOP guns in the turrets, a 35 mm Gökdeniz close-in weapon system (CIWS) at the stern, and Roketsan’s LEVENT RAM launcher with a capacity of 21 missiles.
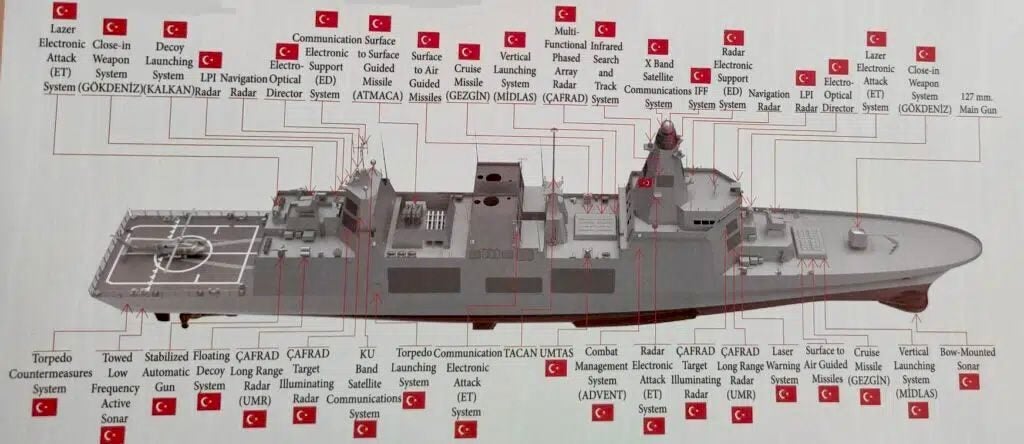
In addition to all these, the new design of the TF-2000 destroyer includes a laser warning system, LPI Radar, Navigation Radar, Electro-Optical Director, Combat Electronic Support System, ÇAFRAD Multi-Function Radar, Infrared Search and Tracking System, X Band Satellite Communication System, IFF System, Radar Electronic Support System, Torpedo Jamming and Deception System and ADVENT Combat Management System.
The TF-2000 project, the final phase of the MİLGEM Program, was initiated in July 2017 to meet the Turkish Navy’s air defense destroyer needs. The project will include the construction of four air defense destroyers, the design and roadmap studies for which are currently being conducted by the Istanbul Shipyard Command and the Naval Forces Design Project Office. In addition to this number, the construction of four more destroyers will be optional. If all goes as planned, Turkey will have its first TF-2000 destroyer in service in 2027.

Between 2011 and 2018, the Turkish Naval Forces Command received four ADA Class Corvettes built under the first phase of the MİLGEM program. During this time, Turkey successfully exported MİLGEM ADA Class Corvettes to Pakistan and Ukraine. TCG İSTANBUL, the first of the four İSTİF Class Frigates to be manufactured during the second phase of the project, will enter the inventory this year. The additional three I-class frigates, which began production in 2023, will enter service with the Turkish Naval Forces in the first quarter of 2026.

