Kuwait Naval Force To Procure Double Eagle SAROV Remotely Operated Underwater Vehicle From Saab
The US Navy has awarded a contract to Sweden-based aerospace and defense company Saab for the Double Eagle Semi-Autonomous Remotely Operated Vehicle (SAROV) for the Kuwaiti Navy. The US Navy is procuring this system for the State of Kuwait Naval Force as a Foreign Military Sales (FMS) program.

Killian Swift, Saab’s Executive Vice President and President of the Middle East and Africa Region, stated, “Saab’s journey in the Middle East has seen growth over the years. Today, we extend our partnerships in Kuwait, leveraging a highly capable, robust solution. “Committed to excellence, we are dedicated to delivering substantial value and enhanced offerings, ensuring we consistently meet and exceed our customers’ evolving requirements,”
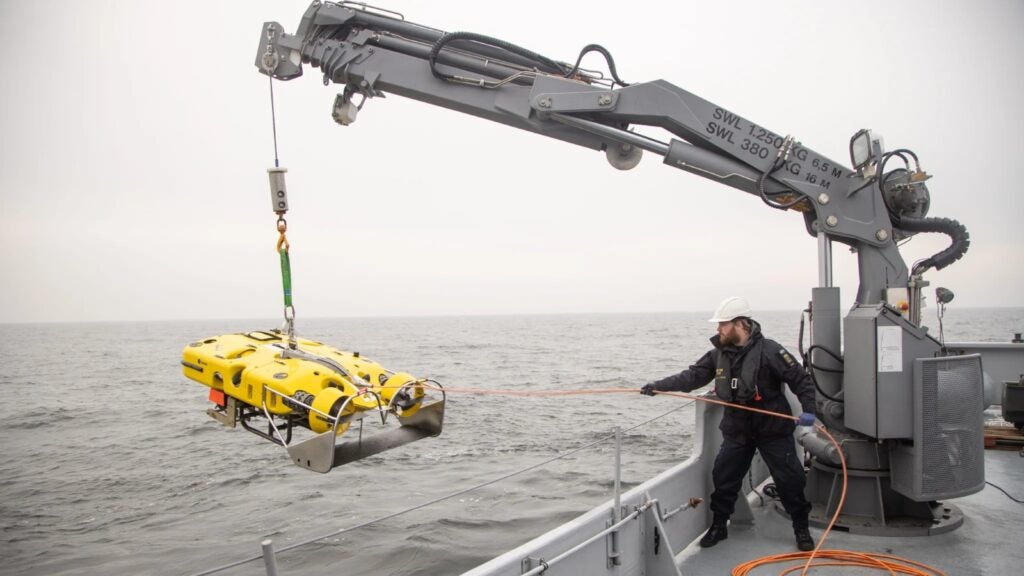

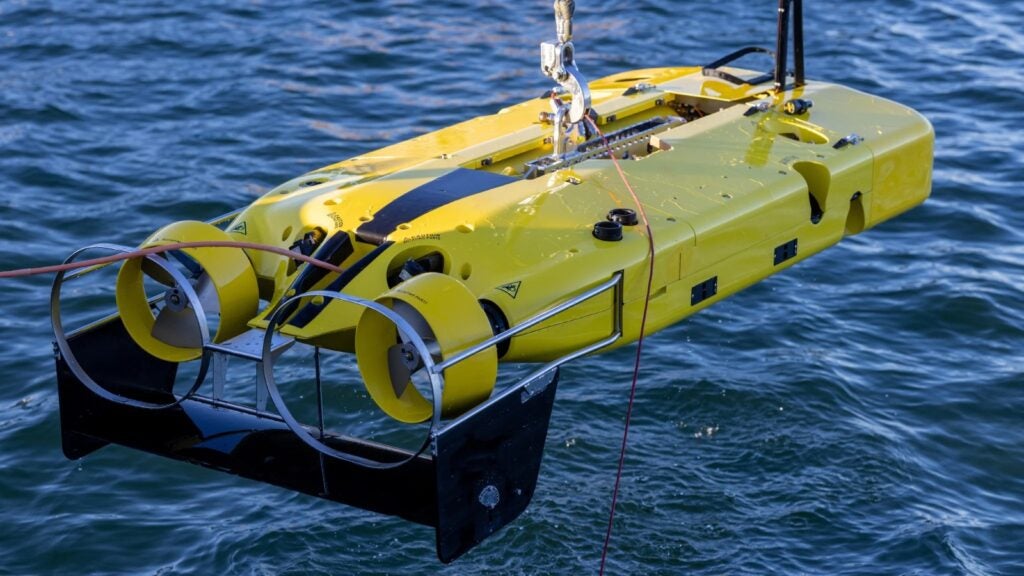
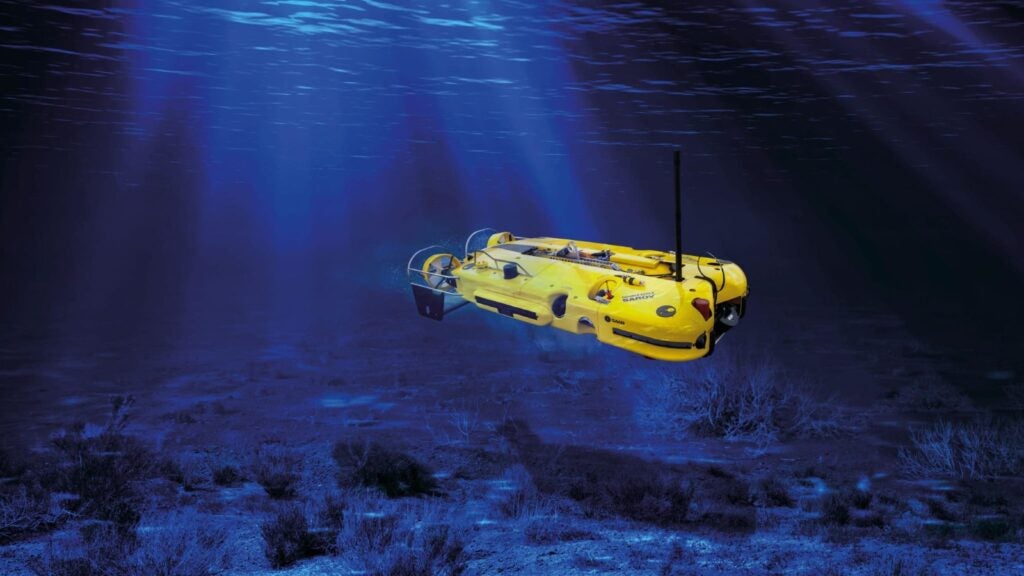
The Double Eagle family of ROVs is a safe and operationally proven ROV system used by navies worldwide. This unmanned underwater vehicle family is separated into three basic configurations: MDS, SAROV, and MuMNS. Double Eagle SAROV, preferred by the Kuwaiti Navy, is a hybrid system capable of performing a variety of operations such as underwater surveys, object identification, mine disposal, and Rapid Environmental Assessment (REA) missions. The system can be employed as a mine disposal ROV or as an AUV for detection, classification, and identification. The SAROV system can be deployed as a fully containerized system or installed on ships due to its versatile design and mission modularity. A special operator plans missions and operates the deployed vehicle while they are on board. The SAROV system can be independently operated with onboard operator software, or it can be fully integrated with a ship’s Combat Management System (CMS).
Using two different tethers, the SAROV vehicle can be operated as a ROV during undersea operations. One uses a thin fiber tether for long-range (>3 km) missions and real-time communication while the vehicle is powered by its internal battery. For long endurance missions, the other tether combines power and communication capabilities with a standard length of 1,000 meters. With its obstacle avoidance capability, the AUV can function independently of the ship and carry out MCM missions using pre-planned instructions that can be downloaded prior to launch or relayed wirelessly while the vehicle is surfaced.